What is Strategic Management?
Strategic management is a continuous process that involves attempts to match or fit the organisation with its changing environment in the most advantageous way possible.
Table of Content
Strategic management is nothing but planning for both predictable as well as unfeasible contingencies. It is applicable to both small as well as large organizations as even the smallest organization face competition and, by formulating and implementing appropriate strategies, they can attain sustainable competitive advantage.

Strategic Management is a way in which strategists set the objectives and proceed about attaining them. It deals with making and implementing decisions about future direction of an organization. It helps us to identify the direction in which an organization is moving.
Strategic management is a continuous process that evaluates and controls the business and the industries in which an organization is involved, evaluates its competitors and sets goals and strategies to meet all existing and potential competitors and then re-evaluates strategies on a regular basis to determine how they are implemented and whether it was successful or does it needs replacement.
Another role of strategic management is to keep a continuous eye on the goals and objectives of the organization.
Definition of Strategic Management
The following statements offer a number of workable definitions of strategic management:
Elements of Strategic Management
Strategic management, as minimum, includes strategic planning and strategic control. Strategic planning describes the periodic activities undertaken by organizations to cope with changes in their external environments (Lester A. Digman). Strategic planning consists of formulating strategies from which overall plans for implementing the strategy are developed.
Further, strategic planning involves formulating and evaluating alternative strategies, selecting a strategy and developing detailed plans for putting the strategy into practice. Strategic control consists of ensuring that the chosen strategy is being implemented properly and that it is producing the desired results. Based on Robert Anthony’s framework, three types of planning and control are required by organizations:
Strategic Planning and Control
This is the process of deciding on changes in organizational objectives, in the resources to be used in attaining these objectives, in policies governing the acquisition and use of these resources and in the means (strategies) of attaining the objectives. Strategic planning and control involve actions that change the character or direction of the organization.
Management Planning and Control
This entails the process of ensuring that resources are obtained and used efficiently in the accomplishment of the organizations objectives. Management planning and control is carried on within the framework established by strategic planning and is analogous to operating control.
Technical Planning and Control
This is the process of ensuring efficient acquisition and use of resources, with respect to those activities for which the optimum relationship between outputs and resources can be accurately estimated (e.g. financial, accounting and quality controls).
Another important term in the study of strategic management is long range planning. Long-range planning, planning for events beyond the current year, is not synonymous with strategic management (or strate- 213 gic planning).
Notall long-range planning is strategic. Certain strategic actions and reactions can be relatively short range and may include more than just planning aspects. It is perfectly reasonable to have long range operating or technical plans that are not strategic. However, it should be noted that most strategic decisions have long-term ramifications.
Scope and Dimension of Strategic Management Strategic management focuses on the total enterprise. It involves the planning, directing organizing and controlling of the strategy-related decisions and actions of the business.
Scope and Dimension of Strategic Management
Strategic management focuses on the total enterprise. It involves the planning, directing organising and controlling of the strategy-related decisions and actions of the business.
Scope of Strategic Management
J. Constable has defined the area addressed by strategic management as “the management processes and decisions which determine the long-term structure and activities of the organisation.”
This definition incorporates five key themes:
Management process
Management processes relate to how strategies are created and changed.
Management decisions
The decisions must relate clearly to a solution of perceived problems (how to avoid a threat, how to capitalize on an opportunity.
Time scales
The strategic time horizon is long. However, for a company in real trouble, it can be very short.
Structure of the organization
An organization is managed by people within a structure. The decisions resulting from the way that managers work together within the structure can result in strategic change.
Activities of the organization
This is a potentially limitless area of study and we normally shall center upon all activities which affect the organization.
These all five themes are fundamental to the study of the strategic management field.
Dimensions of Strategic Management
Strategic management process involves the entire range of decisions. Typically, strategic issues have six identifiable dimensions:
- Strategic issues require top-management decisions. Strategic issues involve the allocation of large amounts of company resources.
- Strategic issues are likely to have significant impact on the long-term prosperity of the firm.
- Strategic issues are future oriented.
- Strategic issues usually have major multi functional or multi business consequences.
- Strategic issues necessitate consideration of factors in the firm’s external environment.
Strategic Management Process
The basic of Strategic Management Process is to explain about organizational strategy. It involves strategies that are processed by managers to make certain choices which make the organization to get better performance.
It is a regular process which shoots up the business or industries where an organization is present by appraising its competitors by regular goals for current or future competitors. It contains following four steps:
Environmental Scanning
It is a method of gathering, scrutinizing and showing information which could be utilized for strategic purposes by finding internal and external factors which can influence an organization.
Strategy Formulation
It is a part of action which plans for correct course of action in order to achieve organisational objectives and purpose. With this, the managers will prepare a corporate, business or functional policies.
Strategy Implementation
It is a way by which a work strategy intends an organization to make particular plan into action.
Strategy Evaluation
This is the last process involved in strategy management process where main strategy calculations are done by appraising internal and external factors which may be grass roots of current strategies.
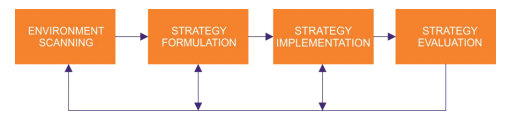
It is an on-going process which should realized every component to interact with other components.
Importance of Strategic Management
A number of reasons are given by authors to as why organizations should engage in strategic management. Many research studies show both financial and non financial benefits which can be derived from a strategic-management approach to decision making.
The importance of Strategic management are :
Financial Benefits
The question, “why should an organization engage in strategic management?” must be answered by looking at the relationship between strategic management and performance. Research performed by Eastlack and McDonald (1970), Thune and House (1970), Ansoffetal (1971), Karger and Malik (1975) and Hofer and Schendel(1978) indicates that formalized strategic management (strategic planning) does result in superior performance by organizations.
Each of these 215 studies was able to provide conceiving evidence of the profitability of strategy formulation and implementation. The formalized strategic management process does make a difference in the recorded measurements of profits, sales and return on assets.
Organizations that adopt a strategic management approach can expect that the new system will lead to improved financial performance.
Non financial Benefits
Regardless of the profitability of strategic management, several behavioral effects can be expected to improve the welfare of the firm. Yoo and Digman emphasize that strategic management is needed to cope with and manage uncertainty in decision-making. They present several benefits of strategic management:
- It provides a way to anticipate future problems and opportunities.
- It provides employees with clear objectives and directions for the future of the organization.
- It results in more effective and better performance compared to nonstrategic management organizations.
- It results in more effective and better performance compared to nonstrategic management organisations.
- It increases employee satisfaction and motivation.
- It results in faster and better decision making.
- It results in cost savings.
Strategic Decisions
Strategic decisions are the decisions that are concerned with whole environment in which the firm operates the entire resources and the people who form the company and the interface between the two.
Characteristics/Features of Strategic Decisions
- Strategic decisions have major resource propositions for an organization. These decisions may be concerned with possessing new resources organizing others or reallocating others.
- Strategic decisions deal with harmonizing organizational resource capabilities with the threats and opportunities.
- Strategic decisions deal with the range of organizational activities. It is all about what they want the organization to be like.
- Strategic decisions involve a change of major kind since an organization operates in ever-changing environment.
- Strategic decisions are complex in nature.
- Strategic decisions are at the top most level, are uncertain as they deal with the future and involve a lot of risk.
Strategic decisions are different from administrative and operational decisions. Administrative decisions are routine decisions, which help or rather facilitate strategic decisions or operational decisions. Operational decisions are technical decisions, which help execution of strategic decisions.
To reduce cost is a strategic decision achieved through operational decision of reducing the number of employees and how we carry out these reductions will be administrative decision.
Strategic Decisions, Administrative Decisions and Operational Decisions
The differences between Strategic, Administrative and Operational decisions can be summarised as follows:-
Table Differences between Strategic, Administrative and Operational decisions
| Strategic Management S. No | Strategic Decisions | Administrative Decisions | Operational Decisions |
| 01. | Strategic decisions are long-term decisions. | Administrative decisions are taken daily. | Operational decisions are not frequently taken |
| 02. | These are considered where the future planning is concerned. | These are short term based decisions. | These are medium-period based decisions. |
| 03. | Strategic decisions are taken in accordance with organizational mission and vision. | These are taken according to strategic and operational decisions. | These are taken in accordance with strategic and administrative decision. |
| 04. | These are related to overall counter planning of all organizations. | These are related to working of employees in an organization. | These are related to production. |
| 05. | These deal with organisational growth. | These are in welfare ofemployees working in an organisation. | These are related to production and factory growth. |
SWOT
The meaning of SWOT is Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats. They are considered as internal factors that has certain control. From the above explanation of SWOT, where Opportunities (O) and Threats (T) are known as external factors on which there is no control.
SWOT Analysis
Basically it is seen that SWOT Analysis is applied in case of audit and analysis of overall strategic position of a concern. It is a powerful tool which focus is on finding strategies which could create firm specific business model which could be best viewed as organizational resources.
This tool, views all positive and negative factors that can be inside or outside the firm which plays an important role in success of an organization.

Strengths
It is an important quality which allows meeting organization operations. It is the base on which the success of an organization depends. It can be tangible or intangible. The important examples of organisational strengths include big financial resources, broad product line, no debt, committed employees, etc.
Weaknesses
It is another quality which keeps away from completing operation and achieving full possibilities. These are factors that do not meet the required standards and can be depreciating machinery, insufficient research and development facilities etc. This quality can be controlled by minimizing or by eliminating. It can be seen that in order to conquer on old machinery, the new machinery are purchased.
Opportunities
Such type of quality is present inside our environment in which it works. Such quality will come up when an organisation takes the advantage of certain conditions in an environment in order to plan and work on certain strategies which makes us more profitable.
Threats
It appears when conditions in an external environment will put on risk in terms of dependability and productivity of an organisational business. The common example of threat will include turbulence among employees, on-going technology change and more competition with over capacity, etc.
Advantages of SWOT Analysis
There are certain advantages of SWOT Analysis:
- Source of information for strategic planning.
- Constructs organizations strengths.
- Reverse its weaknesses.
- Maximize response to opportunities.
- Overcome organizations threats.
- Locating core competencies of firm.
- Setting of objectives for strategic planning.
SWOT Analysis Framework

Limitations of SWOT Analysis
There are certain limitations about SWOT Analysis such as:
- Price increase
- Inputs/raw materials
- Government legislation
- Economic environment
- Locating new market for product which has no overseas market due to import restrictions
Apart from these, there are certain internal limitations of SWOT analysis which are:
Insufficient research and development facilities.
- Faulty products due to poor quality control.
- Poor industrial relations.
- Lack of skilled and efficient labor.
BCG Matrix
Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix is a four celled matrix (a 2 * 2 matrix) developed by BCG, USA. It is the most renowned corporate portfolio analysis tool. It provides a graphic representation for an organisation to examine different businesses in its portfolio on the basis of their related market share and industry growth rates.
It is a two dimensional analysis on management of SBU?s (Strategic Business Units). In other words, it is a comparative analysis of business potential and the evaluation of environment.
BCG Matrix Analysis
According to this matrix, business could be classified as high or low according to their industry growth rate and relative market share.
Relative Market Share = SRI: Sales this year leading competitors sales this year Market Growth Rate = Industry sales this year — Industry Sales last year Consider the four cells of matrix as shown in fig 3.4 where stars, cash cows, question marks and dogs are located. Each of these cells represents a particular type of business.

Stars
In this matrix, stars shows business units that carries big market shares in fast upcoming industry. Instead of generating cash as of fast growing market, the stars need heavy investment so as to meet their lead. In this the SBU?s placed in cell attract since they are located in robust industry.
Cash Cows
The Cash Cows shows business units with big market shares so as to become mature in a slow growing industry. They needs small investment and can obtain cash which are used for investment in other business units.
Question Marks
These units have less market shares and requires great big amount in order to maintain market share. They are normally new products and services that having great commercial aspects.
Dogs
These show weak symptoms of market shares in a low growth market. Such type of units neither obtains cash nor needs big amount of cash. Because of less market share, such business units face lots of cash loss. Such type of business establishment have weaker market share as of more costs with lack of quality and poor marketing.
Limitations of BCG Matrix
It is seen a BCG Matrix will generate a framework where resources are allotted for different business units which made possible in order to compare certain business units instantaneously.
They have certain limitations such as:
- They arranged business as low and high whereas medium also.
- It does not explain about the clearly of market model.
- As studied high market share not always tends to more profits as extra cost is also involved.
- Towards profitability, factors such as growth rate and market share are not the only indicators.
- It is found that many times dogs might help certain business in achieving many advantages as they can get more than cash cows.
FAQ
What is Strategic Management?
Strategic management is a continuous process that involves attempts to match or fit the organisation with its changing environment in the most advantageous way possible.
What is SWOT?
The meaning of SWOT is Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats. They are considered as internal factors that has certain control. From the above explanation of SWOT, where Opportunities (O) and Threats (T) are known as external factors on which there is no control.