What is Consumer Behavior?
Consumer Behaviour is also known as buyer behavior. It is defined as how customer search for, purchase, use, evaluate and disposed of purchased products and services. Consumer behavior focuses on how they make the purchase decisions to spend their available resources (Time, Money, Efforts).
Table of Content
- 1 What is Consumer Behavior?
- 2 Factors Influencing Consumer Behaviour
- 2.1 Cultural Factors
- 2.2 Culture
- 2.3 Subculture
- 2.4 Social Class
- 2.5 Social Factors
- 2.6 Personal Factors
- 2.7 Gender
- 2.8 Age and life cycle
- 2.9 Occupation
- 2.10 Personality
- 2.11 Lifestyle
- 2.12 Psychological Factors
- 2.13 Perception
- 2.14 Motivation
- 2.15 Physiological needs
- 2.16 Safety needs
- 2.17 Social needs
- 2.18 Esteem needs
- 2.19 Self–Actualization
- 2.20 Learning
- 2.21 Experiential Learning
- 2.22 Conceptual Learning
- 2.23 Emotions
- 2.24 Belief
- 2.25 An Attitude
- 3 Five Stage Model of Buying Process
That includes Questions like what they buy, why they buy, when they buy, where they buy, howoftentheyuse it, how they evaluate it after the purchase and the impact of such evaluation on future purchases and how they dispose of it.
Factors Influencing Consumer Behaviour
Influencing factors are as below :
Cultural Factors
Culture
Culture is an important characteristic of a society that distinguishes it from other societal groups. Culture influences the behavior of the can be seen in that transmits from one generation to another. Culture diversity operates in dress, food habits, marriage practices and almost all matters of the individual’s life.
It manifests through various symbols and ritual which are unique to the society. Example : The Turban is a symbol of Sikh culture, a kumkum/ bindi the symbol of Hindu women. The do’s and don’t s listed by culture impact the individual’s lifestyle and consequently his buying behavior.
Subculture
The intensity of the impact will vary from society to society or group to group. Understanding of the culture is helpful to the marketer in–sizing up segments of buyers on the basis of cultural attributes. It helps culture specific marketing effort, which usually produces better results.
The Culture includes smaller groups of sub–culture which is formed on the basis of demographic characteristics, geographic regions, national and ethnic background, political beliefs and regional belief. Subculture is the homogeneous group of people who shares the elements of the overall culture as well as cultural elements unique to their own group.
Social Class of people, who are equal in status. These people socialize among themselves both formally and informally and who shares behavioral norms. Social class is determined by occupation, income, education etc.
Reference Group
A person’s reference group are all the group that have a direct (face to face) or indirect influence on their attitude or behavior. “Reference Group is a group that serves as a reference point for an individual in the formation of his/her beliefs, attitudes and behaviour.
Reference groups are basically small in size and differ from one individual to another. Family members, relative, friends, colleagues and other close acquaintance are usually termed as reference group.
Marketers frequently advertise their products in a group setting – the family eating breakfast cereals, the neighbor admiring the paint of the house.
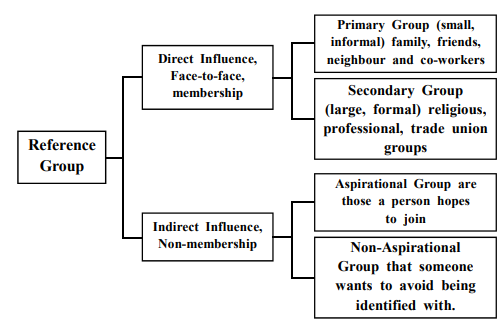
Primary Groups
Primary groups are basically ones whose members are closely knit. Family and relatives fall in this group. These people from primary groups may have a direct and strong impact in your lives and your buying decisions since they are very significant to you.
Primary groups make you comfortable and give you a feeling that they are with you when you are confused about a purchase. These people give you very honest and clear advice’s as they are so close to you, due to which you could be more confident about the purchase.
Secondary Groups
Secondary reference groups are usually formal and they speak less frequently. They may be membership in clubs where the meeting may happen only once a while. In secondary reference groups the power to influence people is quite less as compared to primary reference groups as people in these groups are not that comfortable in sharing their thoughts or views on the purchase.
Aspirational Groups
Aspirational group is the one to which a person may want to become part of. They currently are not part of that group but wish to become and get with that group. For doing the same, they try to dress, talk, act and even think the way the members of that group do. For example, people who like Madhuri Dixit wish to become like her and meet her and so start purchasing and using all those products that she endorses.
Non–Aspirational Groups
The people in these groups are totally opposite to the people in the aspirational group. Here people deny of becoming or getting connected to a particular group. They just hate being related to that group.
Thus marketers need to understand the likes and dislikes of the consumers and also the groups to which they belong. Marketers should recognize the extent to which a reference group influences the consumer and he should also understand out of all the groups which group influences him the most.
Opinion Leader
Is the person who offers informal advice or information about a specific product or produce category, such as which brands is best or how a particular product may be used.
Cliques
Are small groups, whose members interact frequently. They are similar and their closeness facilitates effective communication but also insulates the clique from new ideas. The challenge is to create more openness so cliques exchange information with others in society.
This openness is helped along by people who function as liaisons and connect two or more cliques without belonging to either and by bridges, people who belong to one clique and are linked to a person in another.
Family
Family members are the most influencing factor in consumer buying behavior. In a family parents and siblings are considered most influential.
E.g. : A family that strongly values good health will have a grocery list distinctly different from that of a family that views every dinner as a gourmet event.
Moreover, the family is responsible for the socialization process, the passing down of cultural values and norms to children. Children learn by observing their parents’ consumption patterns, and so they will tend to shop in a similar pattern.
Following are the roles in the family decision making process ?
Influencers
Influencers are the ones who give ideas or information about the product or service to the consumer.
Gate Keepers
Gatekeepers are the family members who usually panel the information. They can be our parents or siblings too who can in any form provide us the information about the product.
Decision Makers
Family or our parents who usually have the power to take decisions on our behalf are the decision makers. After completing the research they may decide to purchase the particular or dispose it.
Buyers
Buyer is the one who actually makes the purchase of the product.
End Users
The person who finally uses the product or consumes the service is the ultimate consumer also called as End user as per the context.
Personal Factors
Gender
There is physiological difference between men and women and because of which they have different needs. For Example : Health and beauty product. Men and Women plays a distinct cultural, economic and social role in the society and this have effect on their decision–making process also.
Age and life cycle
At all stage in life people buy or prefer goods and service. Depending on the age of a consumer, it is a general indication on what product he or she may be interested in purchasing. Consumer tastes in food, clothing, car, furniture and recreation are often age related.
A bachelor would prefer spending lavishly on items like beer, bikes, music, clothes, parties, clubs and so on. A young single would hardly be interested in buying a house, property, insurance policies, gold etc. An individual who has a family, on the other hand would be more interested in buying something which would benefit his family and make their future secure.
Occupation
According to occupation the preference changes. Occupation affects the person choice in selection of product and services. Blue–collar workers tend to buy more rugged work clothes; whereas white–collar executives buy more business suits. A company can even specialize in making products needed by a given occupational group.
- Ramesh was working with an organization as Chief Executive Officer while Jayesh, Ramesh’s friend now a retired professor went to a nearby school as a part time faculty. Ramesh always looked for premium brands which would go with his designation whereas Jayesh preferred brands which were not very expensive. Ramesh was really conscious about the clothes he wore, the perfume he used, the watch he wore whereas Jayesh never really bothered about all this.
- That is the importance of one’s designation. As a CEO of an organization, it was really essential for Ramesh to wear something really elegant and unique for others to look up to him. A CEO or for that matter a senior professional can never afford to wear cheap labels and local brands to work.
- An individual’s designation and his nature of work influence his buying decisions. You would never find a low level worker purchasing business suits, ties for himself. An individual working on the shop floor can’t afford to wear premium brands to work.
- College goers and students would prefer casuals as compared to professionals who would be more interested in buying formal shirts and trousers.
Personality
Personality defined in terms of traits like self– confidence, dominance, autonomy, deference, sociability, defensiveness and adaptability. Brands also have personality and consumers are likely to choose brand which matches there personality consistent with actual self–concept.
Lifestyle
Life means a person pattern of living. Though people came from same culture, sub–culture, social class or occupation but their pattern of living may be different. Lifestyle can be expressed in terms of person’s activities, interest and opinions. For example when a consumer leads a healthy lifestyle, then the products he buys will relate to healthy nearishments.
Psychological Factors
An individual’s buying decisions are further influenced by psychological factors : Perception, motivation, learning, belief and attitude.
Perception
A stimuli is any unit of input affecting one or more of the five senses : sight, smell, taste, touch, and hearing. The process by which we select, organize and interpret these stimuli into a meaningful and coherent picture is called perception. In essence, perception is how we see the world around us and how we recognize that we need some help in making a purchasing decision.
E.g., when a retail clothing store has displayed clothes in crowded racks using low quality plastic hangers, customers get a perception that it is a low–quality brand. But when the same clothes are presented well with back–lit mannequins, neatly arranged, good quality attractive hangers, etc. the customers build a different perception about the brand.
Motivation
When you buy a product, you usually want to fulfil your some kind of need. These needed becomes motive when aroused sufficiently.
E.g. : Suppose you are hungry and you stop to have Vadapav. In this case, you are motivated by hunger to stop at Vadapav shop. Motives are the driving force that causes a person to take action to satisfy specific needs. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, which has arranged needs in ascending order of importance physiological, safety, social, esteem, self–actualization needs.
Physiological needs
Are basic needs like hunger, thirst, shelter. Advertisements showing pizza and juice after marathon are examples of appeals to satisfy hunger and thirst.
Safety needs
Includes security and freedom from pain and discomfort. E.g. : Aware of the aging population health fears, there medical centre advertises that they offer consumers a full body scan for early detection of chronic diseases.
Includes sense of belonging, love. Advertisements for clothes, cosmetics and vacation package suggest that buying the product can bring affection.
Esteem needs
Include self–respect and sense of accomplishment, prestige, fame and recognition. Esteem needs are the basis for the human desire we all have to be accepted and valued by others. Mont Blanc pens, Mercedes–Benz automobiles stores all appeal to esteem needs.
Self–Actualization
Self–actualization needs are the highest levels in Maslow’s hierarchy, and refer to the realization of a person’s potential, self–fulfilment, seeking personal growth and peak experiences. Even so advertisement may focus on this type of need.
E.g. : Microsoft appealed to consumers’ needs for self–actualization when it chose “Your Potential our passion” as the windows XP slogan.
Learning
Consumer behaviour is the results from learning, which is the process that creates changes in behaviour through experience and practice. It is not possible to observe learning directly, but we can infer when it has occurred by a person’s action.
E.g., suppose you see an advertisement of a new improved headache medicine, you go to the store that day and buy that medicine. We infer that you have learned something about the medicine. There are two types of learning.
Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is a type of learning when experience changes your behaviour.
Conceptual Learning
It is a second type of learning, which is not acquired by direct experience. Imagine that you are standing near chocolate vending machine and have notice diet chocolate with no sugar content.
As someone has told you that diet chocolate leaves a bad after– taste, you choose a different chocolate. You have learned that you would not like new sugar free chocolate without ever trying it.
Emotions
Companies develop advertisements that are emotional which invoke different kind of feelings. Consumer response is not always cognitive or rational. Cadbury’s advertisements are very emotional and touches ones’ heart. An emotion–filled brand story has been shown to trigger’s people desire to pass along things they hear about brands, through either word of mouth or online sharing.
Belief
Is an organized pattern of knowledge that an individual holds as true about his or her world. A consumer may believe that Apple i–phone is durable, touch screen is smooth, and is reasonably price according to its features. This belief is based on the knowledge and faith the consumer has for the product.
Consumer tends to develop belief about the product attributes and then, through these beliefs, form a brand image– a set of beliefs about a particular brand. In turn, the brand images shape consumers attitudes towards the product.
An Attitude
Is a learned tendency to respond consistently towards a given object, such as a brand. Attitudes rest on the individual value system, which represents personal standards of good and bad, right and wrong, therefore, attitude tend to be more enduring and complex than beliefs. E.g. : Attitude towards using credit card for purchase across world.
Five Stage Model of Buying Process
The below mention five stage which consumer goes through while making purchase.

Need Recognition
Consumer will not able to purchase the product unless they know what are their needs or want. If they know that they require a particular product then only consumer will buy that product.
Need arises when there is a problem. E.g. : If you break your laptop which you were using it daily, a need arises to purchase new laptop.
Want arises because you are influenced by some external factors. E.g. : If you find your friend using an Apple Laptop, and you might have seen its reviews on Internet, you feel you want to upgrade to an Apple laptop, though you may already have a Dell laptop.
In this case marketer should identify the needs of the consumers and offer the products based on the Desire.
Information Search
After need recognition consumer are aware of their need or want. They know that what product they will buy which will solve their problem. Therefore, he wants to know more about the product and does information search.
When consumers want to buy a laptop, they look for its features, price, discounts, warranty, after sales service, insurance, and other important features. Here, a marketer must offer a lot of information about the product in the form of informative videos, demos, blog, how–to–do videos, and celebrity interviews.
Evaluation of Alternatives
In first and second stage, consumers have done lots of research about the product need and have collected information about the product. Information gathered from various sources is used in evaluating alternatives. There are many products available in the market which can solve the consumer problems. Hence, it is the consumers who have to make a choice after evaluating the various available alternatives.
Purchase Decision/Purchase
In this stage consumer is deciding whether to buy the product or not. Yes, even at this stage consumer can drop the purchase and walk away. Philip Kotler (2009) says, the final purchase decision may be ‘interrupted’ by two factors. Customer may get a negative feedback from friends or other customers who have bought it earlier.
E.g., a customer shortlists a laptop, but his friend gives a negative feedback. This will make him to change his decision. Secomdly, the decision to buy a laptop itself might change.
The Consumer chooses the product that he wants to buy, but many times, he may not actually buy it for various reasons. At this stage, a marketer should find out the various reasons due to which the consumer is hesitating to buy. The reasons could be price, value, and change in the needs of the consumer.
Marketer needs to step up the game. Marketer may start reminding the customers the reason behind their decision to buy the product. Furthermore, give as much information regarding your brand, reiterating that you are the best provider of the product that can fulfill his needs. Re–targeting by simple email reminders can enforce the purchase decision.
Post–Purchase evaluation
After the purchase, a consumer always compares products with their expectations. There can be two outcomes; consumer may be either satisfied or dissatisfied. If the product satisfies the need of the consumer then, they are happy. Otherwise, the consumer will be dissatisfied, and they feel that they have taken incorrect decision.
So, he may want to return of the product or exchange it. Even though customer is satisfied, there is no guarantee that the customer might come again to purchase another product.
A marketer has to make sure that the consumer is satisfied with the product so that his experience will lead to repeat purchase by customers. Brands need to be careful to create positive post–purchase experience.
What is Consumer Behavior
Consumer Behaviour is also known as buyer behavior. It is defined as how customer search for, purchase, use, evaluate and disposed of purchased products and services.