What is Product Life Cycle?
The concept of product life cycle creates distinct stages in product performance in market place as introduction, growth, maturity, saturation and decline phase.The idea of product life cycle is borrowed from biology and an analogy is drawn with the life of an organism.
As a living being progresses through the stages of birth, growth, maturity, decline and death, so also a product passes through similar stages during its market entry and exit.
Product life cycle theory is one of the first analytical attempts to determine marketing strategies at different product market situations. The product life cycle concept describes the stages in the sales (market response) history of a product.
Table of Content
The basic features of this theory have propositions that a product has a limited life and a product’s sales generally follow an ‘S’ curve until sales eventually start declining
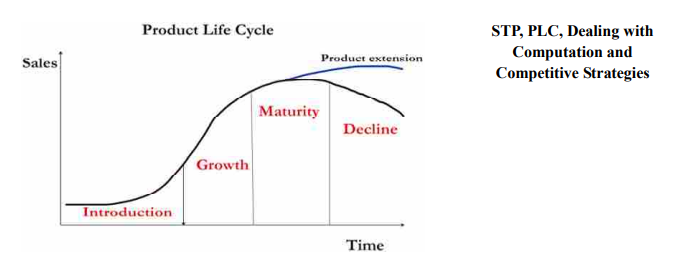
The concept of product life cycle creates distinct stages in product performance in market place as introduction, growth, maturity, saturation and decline phase.
An introduction phase is known as lag phase, the growth phase as exponential phase, growth and maturity as stationary phase and decline as a down turn phase. These are the different stages in a typical product lifecycle.
Extending the Product life Cycle
For successful products, a business wants to do all it can to extend the growth and maturity phases of the life cycle, and delay the decline phase. What can businesses do to extend the product life cycle ? To do that, it may decide to implement extension strategies– which are intended to extend the life of the product before it goes into decline. Extension strategies are :
- Advertising – Try to gain a new audience or remind the current audience.
- Price Reduction – More attractive to customers.
- Adding value – add new features to the current product, E.g. improving the specifications on a smartphone.
- Explore new markets – Selling the product into new geographical areas or creating a version targeted at different segments.
- New packaging – brightening up old packaging or subtle changes.
Shapes of Product Life Cycle
Products go through different life cycle patterns. There are several shapes that can be observed in practice. The shapes commonly reported are classical bell–shaped curve, growth–slump–maturity pattern, cycle– recycle pattern, scalloped pattern; style, fashion and fad. Growth–slump maturity pattern, exhibits an initial growth for the product, followed by a decline in sales and subsequent stability for fairly long time.
Growth–slump–maturity pattern displays a multi– modal shape due to the different promotional mechanisms adopted by the marketers at different points of time.

There are actually four different life cycle curves for the four different types of products :
High–learning
Product is one that requires significant customer education and the introduction stage is extended. You could say that the GPS was a high–learning product. This is because when the GPS first came out, most people were used to either relying on maps or the directions of others.
When the GPS first came out, many people were not sure how to exactly use it. Now, most people always have GPS with them because they come standard in almost every smartphone and new car.
Low–learning
Products are different because their sales begin very quickly due to the simplicity of the product. This allows consumers to understand the product almost right away. Often competitors can easily copy the low–learning products.
Fashion Product
These products change with the style of the times and the life cycles frequently appear in apparel. They usually go from the introduction stage right to the decline and then eventually reappear. This does not mean that each fashion product has the same life cycle.
FAD Products
These fad products experience rapid sales during the introduction phase and then they decline at almost the same speed. These products tend to be novelties with a short life cycle.
Stages of Product Life Cycle
Products follow certain kinds of life cycle patterns. Whether the pattern is like that of an S–shaped curve or modifications as we have hown in previous pages, we need to understand the relevance of the product life cycle concept in the context of making strategic decisions and making marketing forecasts.
While some products fail immediately on birth or a little later, others may live long enough. BPL television launched Picture–in–Picture (PIP) television, which was eliminated at the introduction stage itself. Pagers had a grand launch in the market but got eliminated as the next better product of communication in the form of mobile phones entered the market.
The innovation of a new product and its degeneration into a common product is termed as the life cycle of a product. This often helps competitors to benchmark against the available technology and develops better products compared to the current one so as to take away the market share from the market leader.
There are four distinct stages in the life cycle of a product as shown below :
Introduction Stage
Research or engineering skill leads to new product development. The product is put on the market at the stage of commercialization. The concept of product life cycle starts from the ‘commercialization’ stage of new product development.
At this stage, product awareness and acceptance among prospective customers are minimal. As the sales are low, there are high promotional costs. This is due to the fact that the company has to spend money for advertising, sales promotion and other forms of promotion.
The major obstacle to rapid market penetration at this stage is poor distribution strategy. Many retailers will not support a new product launch and will wait till they hear well about the brand.
E.g. : Holographic projection technology allows consumers to turn any flat surface into a touchscreen interface. With a huge investment in research and development, and high prices that will only appeal to early adopters, this is another good example of the first stage of the cycle.
Growth Stage
This stage begins when demand grows rapidly. In the case of repeat buying situation, the innovators move from trial purchase to adoption stage If the innovators are satisfied with the products, they influence other buyers through word–of– mouth and referral communication.
Deeper penetration in market by intensive distribution strategy and increase in store visibility and usage tend to bring new buyers in the market. The competitors also start their advertising and sales promotion making the total category demand to increase in the market. Growth stage also contributes in increasing profit.
E.g. : With advanced technology delivering the very best viewing experience, Blue Ray equipment is currently enjoying the steady increase in sales that’s typical of the Growth Stage.
Organic food is another product which is gaining momentum in the market and is in the growth stage and it has not gained deeper penetration in the market place yet.
Maturity Stage
Sales growth continues, but at a diminishing rate, because of the declining number of potential customers who remain unaware of the product or who have taken no action.
E.g. : Introduced a while back, manufacturers of DVDs, and the equipment had established a strong market share. However, they still had to deal with the challenges from other technologies. That are characteristic of the Maturity Stage.
Decline Stage
Eventually, sales start declining due to multiple reasons. Changes in customer preferences, competition in the market, technology and other environmental forces lead to the decline of sales. Sales begin to diminish as the customers begin to get bored with the product.
E.g. Dial telephones and petrol jeeps led to eventual dropping of the product by the firms. The product decline happens due to entry of new competitors with advanced technology; and reduction in consumer interest.
The marketer is left with an option of price reduction, putting pressure on the profit margins and leading to deletion of products.
E.g. : Typewriters, and even electronic word processors, have very limited functionality. With consumers demanding a lot more from the electronic equipment they buy, typewriter is passing through the final stage of the product life cycle.
Product Startegy For Life Cycle Stages
Characteristics and Marketing Strategies at Introduction Stage The product life cycle begins with the introduction stage when the product is launched. At this stage :
- Sales are low. This stage involves high distribution and promotion expenses; profits are found to be negative or low. Since it is too early for improvements, basic versions of the product are sold.
- The second possible alternative strategy is low price and promotion. This will help in cornering a bigger market share and faster market penetration. This strategy is possible when the size of the market is big and buyers are sensitive to price.
- The marketer passes the economy of scale of operation to customer and follows a low cost per unit production process.
- At this stage, since the product is new, all focus is on building distribution network and product awareness. Characteristics and Marketing Strategies at Growth Stage.
Charactistics and Marketing Strategies of Growth Stage
- This stage is most rewarding for the marketer, if the new product is considered to be satisfactory by the market. The characteristics of this stage include a very sensitive market response where sales climb rapidly.
- The growth stage has two distinct sub–stages – early and late growth. In the early growth stage, the sales increase at an increased rate and in the late growth stage it increases at a decreasing rate.
- At the growth stage, the marketer follows different kinds strategies compared to the earlier stage of product life cycle.
- Increased emphasis on promotions will play a very important role in educating the market as well as in meeting the challenges of the competition.
Characteristics and Marketing Strategies at Maturity Stage
At the end of a responsive growth stage, begins a stage of maturity.
- In this stage despite higher spending on the marketing program there is no substantial growth in sales volume and the market is flooded with many competing products.
- In this stage, though the sales growth slows down, the stage itself continues for a long period. Therefore, it poses a strong challenge to Marketing Managers.
- The market experiences commoditization and competition brings down the prices, putting pressure on the profitability and liquidity of the firm. In the late maturity stage, the profits drop sharply.
- Due to intense competition and falling profits, not many companies can survive this stage. Thus, a number of proactive steps are needed to stay profitable.
- A market modification strategy, the companies have goals to increase the consumption; hence the companies look for new users, new market.
- The other alternative strategy is to bring product modifications like improvement in quality, features and style.
Characteristics and Marketing Strategies at Decline Stage
- There is a saying that “nothing lasts forever” or “all good things must come to an end”. This is also applicable to successful products and services in the market.
- The sale of any product eventually dips. The plunge continues for some years. This indicates the stage of decline.
- This is the stage when the product is left with very few customers and these customers are called laggards. This is a stage when many of the existing customers switch to newer and better brands in the market.
- The firm reaches this stage due to lack of strategies. A company may have a number of products introduced simultaneously where the extent of decline may not be the same for all the products.
- The company can decide to follow a strategy to maintain its position in the market in territories where it is doing well.
- Alternatively, the company can decide to harvest the market. This strategy is aimed at reducing the overall costs including production, maintenance, advertising and sales force management costs and hoping that the product sales will be profitable for some time more.
- Eventually the firm will decide to drop the product from its portfolio. This is the end of the line for a particular product. However, it may be sold to another company if there s a buyer.
What is Product Life Cycle?
The concept of product life cycle creates distinct stages in product performance in market place as introduction, growth, maturity, saturation and decline phase.
How many stages are there in Product Life cycle?
There are four Stages of product life cycle are : 1.Introduction Stage, 2.Growth Stage, 3.Maturity Stage and 4.Decline Stage.